|
TERBUTALINE SULFATE |
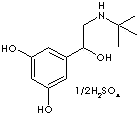
| alpha-((tert-Butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol sulfate; Brethaire; Brethine; Bricanyl; 5-(2-((1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-1,3-benzenediol sulfate; Bricanyl Turbuhaler; 1-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-tert-butylaminoethanol sulphate; 2-tert-Butylamino-1-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl) ethanol; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
23031-32-5, 23031-25-6 (Parent) |
|
EINECS RN |
245-386-3 |
|
FORMULA |
C12H19NO3·1/2H2SO4 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
274.32 |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Bronchodilator / Tocolytic agent |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to off-white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
247 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen oxides. Sulphur oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Target Organ Effect, Teratogen. Target Organs: Lungs, Heart, Nerves. |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XN |
|
RISK PHRASES |
42/43-65 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-36 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Terbutaline is a member of a class of drugs called beta adrenergic receptor agonists (stimulators) that is used for treating asthma and other airway diseases. Other drugs in the same class of drugs include albuterol (Proventil), metaproterenol (Alupent), pirbuterol (Maxair), and salmeterol (Serevent). Asthma is a breathing problem caused by narrowing of air passages (bronchial tubes) through which air moves in and out of the lungs. These airways can be narrowed due to the accumulation of mucus, spasm of the muscles that surround them (bronchospasm), or swelling of their linings due to the accumulation of fluid. Airway narrowing leads to shortness of breath, wheezing, and cough. Terbutaline is a bronchodilator, a medication that dilates (expands) air passages in the lungs. It attaches to beta adrenergic receptors on muscles surrounding the air passages, causing the muscles to relax and dilate the air passages. Wider air passages allow more air to flow in and out of the lungs. Increased airflow reduces shortness of breath, wheezing, and cough. Terbutaline also is used for delaying premature labor by relaxing the muscles of the uterus that are responsible for expelling the fetus at delivery. The FDA approved terbutaline in 1974. (http://www.medicinenet.com/) Ritodrine and terbutaline are sometimes used as tocolytic medicines to slow uterine contractions during preterm labor. Ritodrine and terbutaline are given through a vein (intravenously, or IV) and/or by injection. Use of terbutaline for the treatment of preterm labor is an unlabeled use of the medicine. Terbutaline has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of asthma and other breathing conditions, but it is also widely used to treat preterm labor. The longer ritodrine and terbutaline are used, the less effective they are at stopping contractions (an effect called tachyphylaxis). (http://www.questdiagnostics.com/) Beta-sympathomimetics
- salbutamol
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white powder |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
pass A,B,C |
|
ASSAY |
98.0 - 101.0% |
| ACIDITY |
0.3% max |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.2% max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
| ORGANIC IMPURITIES |
0.5% max |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |